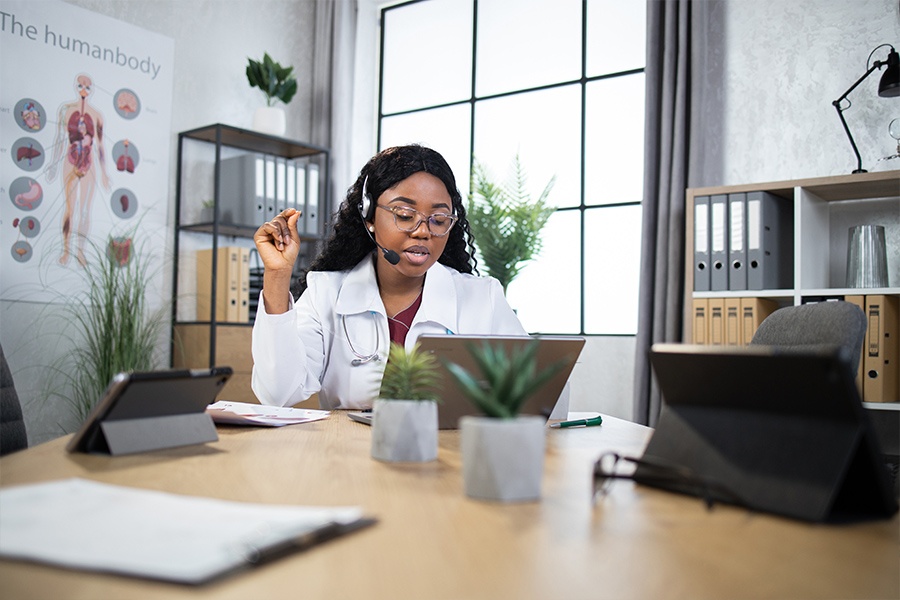
The COVID-19 pandemic has significantly transformed the landscape of healthcare delivery in the United States, with telehealth emerging as a vital solution for maintaining patient care. As of December 2023, a report from the American Medical Association (AMA) highlights the sustained rise in telehealth services, which have become a mainstream option for many patients seeking care for various health issues.
Initially adopted out of necessity during the pandemic, telehealth has proven to be an effective way to provide medical care while minimizing the risk of virus transmission. Patients have embraced the convenience of virtual visits, finding that they can access healthcare professionals without the need to travel or wait in crowded waiting rooms. As a result, both patients and healthcare providers have reported high satisfaction levels with telehealth services.
One of the significant advantages of telehealth is its ability to enhance access to care, particularly for individuals living in rural or underserved areas. Many residents in these regions face barriers to receiving in-person care, including long travel distances, limited healthcare resources, and transportation challenges. Telehealth eliminates many of these obstacles, allowing patients to consult with specialists and primary care providers from the comfort of their homes.
Furthermore, telehealth has expanded its reach beyond primary care to encompass a wide range of specialties, including mental health, chronic disease management, and post-operative care. This versatility allows patients to receive comprehensive care tailored to their needs, regardless of location. Mental health services, in particular, have seen a surge in telehealth utilization, as many individuals find it easier to seek help remotely, reducing the stigma often associated with in-person visits.
Despite the many benefits of telehealth, challenges remain. Issues such as internet access disparities, technology literacy, and reimbursement policies pose barriers to widespread adoption. Many patients, especially older adults and those from low-income backgrounds, may struggle with the technology required for virtual visits. To address these concerns, healthcare providers and policymakers are advocating for improved broadband access and technology training programs to ensure that all patients can benefit from telehealth services.
Additionally, as telehealth becomes more integrated into the healthcare system, discussions about reimbursement and regulatory policies are ongoing. Many healthcare providers are urging lawmakers to extend telehealth coverage beyond the public health emergency status, ensuring that patients can continue to access these services without interruption. The AMA is actively advocating for policies that support the continued growth of telehealth, emphasizing the need for equitable access to care.
As the landscape of healthcare continues to evolve, telehealth is expected to remain a critical component of patient care. The convenience and accessibility of virtual visits have reshaped how healthcare is delivered, offering patients a flexible option that aligns with their needs. As stakeholders work together to address the remaining challenges, there is a strong belief that telehealth will play an increasingly important role in the future of healthcare in the United States.